Brief Description of Rubber Regulating Wheel for Optimal Grinding:
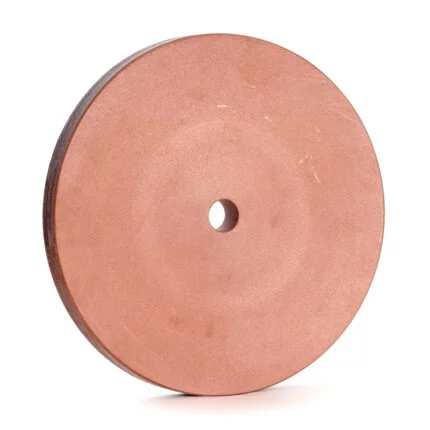
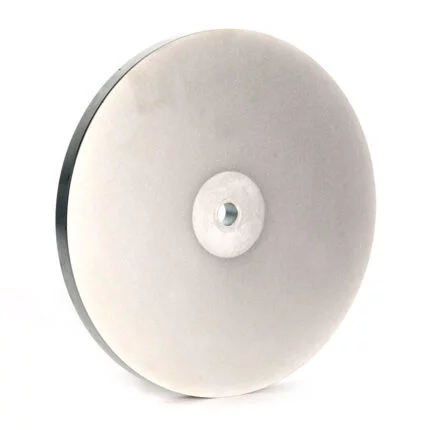
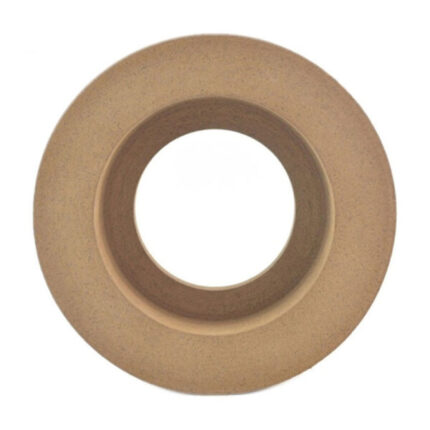
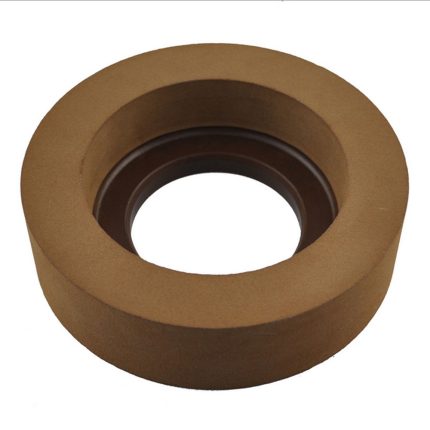
The rubber regulating wheel is abrasive. Its purpose is to keep the workpiece against the grinding wheel, reduce pressure, and control rotation. It is commonly composed of rubber. Rubber regulating wheels are used in centreless grinding as control wheels. Most wheels are with straight and recessed sides with diameters ranging from 50mm to 400mm and thickness from 25mm to 250mm. These regulating wheels are made with a 100 percent natural rubber bond matrix and are built to the tightest specifications. The abrasive grain is held in place by the matrix, which ensures uniform abrasive exposure. These wheels have a strong grip, which allows for high stock removal and steady workpiece rotation. Rubber Bonded Regulating Wheels (also known as Control or Feed Wheels) are made using the rubber calendaring process for the best results. Rubber regulating wheels are widely utilized in the Bearing, Automobile, Hydraulic, and Cutting Tool industries, among others
Features of Rubber Regulating Wheel:
- Longer wheel-life
- Lesser dressing frequency
- Superior form retention
- Superior surface finish
- Optimized efficiency
- Future-oriented
- Increased lifespan with a strong bond and less damage
Detailed Description of Rubber Regulating Wheel:
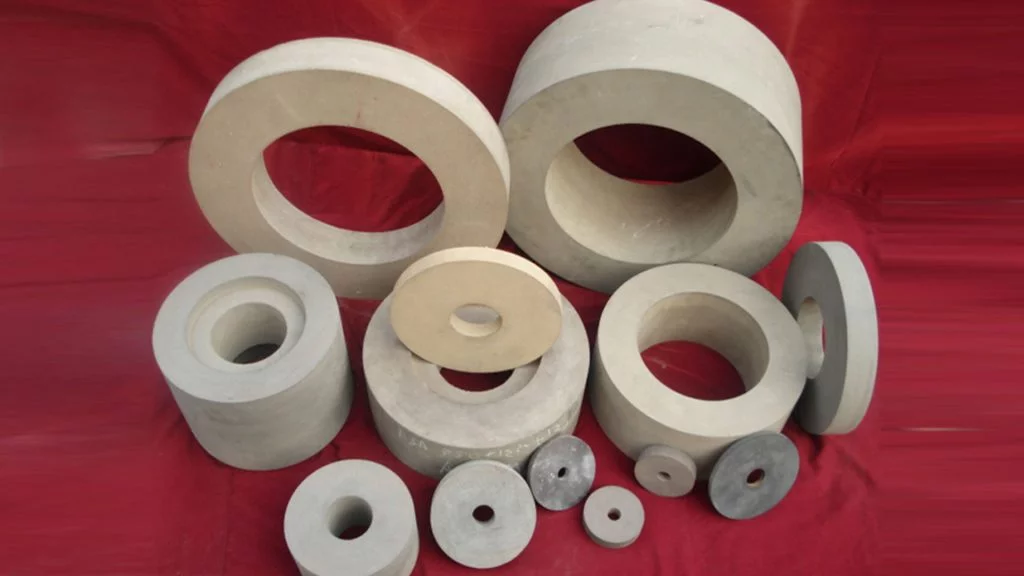

-
Working Principle of Rubber Regulating Wheel in Centerless Grinding:
The workpiece is held between two wheels moving in the same direction at different speeds and a workholding platform in centerless grinding. On a fixed axis, one wheel, known as the grinding wheel, spins such that the force imparted to the workpiece is directed downward, on the workholding platform. The grinding operation is normally carried out by this wheel having a higher tangential speed than the workpiece at the point of contact. The rubber regulating wheel, on the other hand, is a moving wheel. This wheel is used to impart lateral pressure to the workpiece, and it generally has an extremely rough or rubber-bonded abrasive to trap it.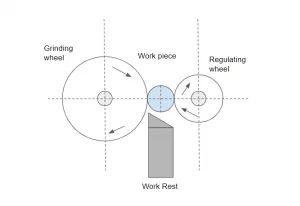
(Working Principle)
The grinding action is provided by the relative speed of the two wheels, which regulates the rate at which material is removed from the workpiece. The workpiece rotates with the rubber regulating wheel throughout the operation, with the same linear velocity at the point of contact and (hopefully) no sliding. The grinding wheel accelerates its rotation, sliding past the workpiece’s surface at the point of contact and eliminating material chips as it goes.
-
Advantages of Rubber Regulating Wheels:
- Continuous processing, no tool retractions, quick clamping of the workpiece, and excellent productivity.
- The bracket and guide wheel placement mechanism is sturdier than the top and center frame of a traditional cylindrical grinding machine, and the stock removal is big, which is ideal for processing thin shaft workpieces. It is also simple to achieve high speed and powerful grinding by using a rubber regulating wheel accompanied by a centerless grinding wheel.
- A rubber regulating wheel is constructed of abrasive material, similar to a grinding wheel, although it is generally coupled with rubber or another comparable substance. A regulating wheel, as the name indicates, controls the speed of a component while it rotates against a grinding wheel. Because a regulating wheel regulates the material removal rate, surface quality, and geometry, it may be more important to the operation than a grinding wheel.
-
Types of Centerless Grinding Processes Accompanied by Rubber Regulating Wheel:
The regulating wheel is typically composed of hard rubber and is abrasive, and its function is to move the component being ground through the grinder via a Through-feed or In-feed procedure. These procedures depend on the working of the rubber regulating wheel.
-
Role of Rubber Regulating Wheel in Through-feed Grinding:
The inclination angle of the rubber regulating wheel is usually between +1 and +3 degrees. The part thru-feed rate in inches per minute is determined by this angle and controlling wheel speed (RPMs ranging from 15 to 300 RPM). The size and length of the component determine the RPM speed. Chatter might occur if the RPM is set too high. If the rubber regulating wheel’s angle is excessively sharp, it might result in uneven wear, taper, and short wheel life. The pieces might stall between the wheels if the regulating wheel is too near to parallel with the grinding wheel.
-
Role of Rubber Regulating Wheel in Infeed grinding:
Infeed centerless grinding, which is comparable to plunge grinding on a center-type machine, is frequently used to grind workpieces with complicated forms. The grinding and rubber regulating wheels must be dressed to meet the part’s intended profile cut, and the workpiece rest blade must be tooled to fit the part’s form. The component is fed into the rubber regulating wheel, which pushes it against the grinding wheel. In contrast to through-feed grinding, the work does not travel axially.

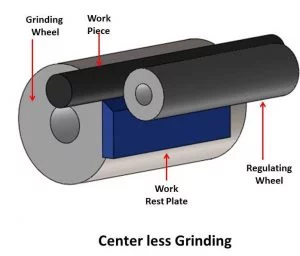
Role of the Work Rest Blade in Supporting Rubber Regulating Wheel:
The work rest blade’s job is to keep the part in contact with the rubber regulating wheel while it’s being machined. On a centerless machine, the centers of the regulating and grinding wheels are usually positioned at the same height, but the center of the workpiece sits higher on the work rest blade. The height of the work rest blade is critical; for example, if the workpiece is positioned too high, it may clatter; if it is set too low, it may be out of round.
Role of Workpiece Angle in Centerless Grinding:
The work rest blade’s top angle is usually 30o, although it can vary from 0 to 45 o. The angle slopes in the direction of the regulating wheel, which drives the portion. In centerless grinding, the angle of the workpiece rest blade is also crucial. A thin wheel of three to four inches in diameter may function well at 30 o, while a broader wheel of six to ten inches in diameter may create too much pressure toward the grinding wheel, generating chatter, and may require a 20o to 25 o angle. The Centerless Grinder is a highly adaptable machine, and the rubber regulating wheel and Work Rest blade are critical to its performance.
-
Manufacturing Process of Rubber Regulating Wheel:
The rubber regulating wheel is one kind of organic bond wheel. Natural or synthetic rubber is used as the primary raw material. Its bonding strength is stronger than that of the resin bond when mixed with abrasive grains such as corundum or carborundum. It can be used to bind very thin grinding wheels or high-elasticity cutting wheels. The concession property is good, particularly at high temperatures, because the pores in the rubber bonding agent polishing sheet are tiny, the voids are small, the structure is tight, and the shape is maintained well. However, due to the rubber bond’s low heat, oil, and moisture resistance, it should be utilized within two years.
-
Installation of Rubber Regulating Wheel:
Before installing the rubber regulating wheel, it must be thoroughly examined. Whether it has cracks or damage. The test should be performed according to the standard before usage. It is completely forbidden to use otherwise. Check the spindle speed on the machine tool before installation, and do not exceed the working speed indicated on the wheel. For tightening the rubber regulating wheel, only a particular nut wrench may be used, and it must be tightened in symmetrical sequence on opposite sides of the main shaft. The nut has to be loose. The use of a supplemental fixture or a tapping tool is prohibited. To avoid the rubber regulating wheel becoming unbalanced, turn off the coolant. The rubber regulating wheel, grinding wheel spindle, and chuck diameters must all fulfill the specifications. In the event of a protective cover, the newly installed grinding wheel must idle at the working speed for the following times: a grinding wheel with an outer diameter of 400 mm must idle for at least 2 minutes, and a grinding wheel with an outside diameter of 400 mm must idle for at least 5 minutes. The operator should not stand in front of the grinding wheel when it is idle.
-
Notes For the Controlled Operation of Centerless Grinding Wheels:
- Before beginning, inspect the machine for damage and do not lay anything on the machine table; instead, carefully position the workpiece.
- Before beginning, check that the oil level in the fuel tank is normal, that the water level in the cooling water tank is normal, that the grinding wheel and the space between the guide wheel and the supporting blade are normal, and that the machine tool is free of debris.
- Before turning on the machine, double-check the switches and make sure the safety features, such as the protective cover, are working.
- Before you begin, clean the centerless grinding wheels and the guide wheel dressing seat, and fill the oil cup with oil.
- The machine, operators should be taught according to the operating instructions to learn about various job methods.
- After the oil meter is steady, check the oil system oil mirror and start the centerless grinding wheel and guide wheel.
Summary:
Rubber regulating wheel is a kind of organic bond wheel that helps grinding wheel for proper grinding. It helps both in cylindrical and centerless grindings. Rubber Bonded Regulating Wheels (also known as Control or Feed Wheels) are made using the rubber calendaring process for the best results. These wheels are superior to retention and provide optimum efficiency. All guides about the use of this wheel, installing precautions, and controlled operation has been provided. You can follow and give read this guide for optimum results.
More customized grinding wheels are available, contact us.
[wpforms id=”4612″]






















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.