Electroplated cutting wheels include an electroplated diamond cutting wheel and an electroplated CBN cutting wheel. The former is mainly used to machine nonmetallic materials characterized by high rigidity, such as glass, ceramic, tungsten carbide, ferrite, etc. The latter is mainly used to machine metal, steel, and similar materials.
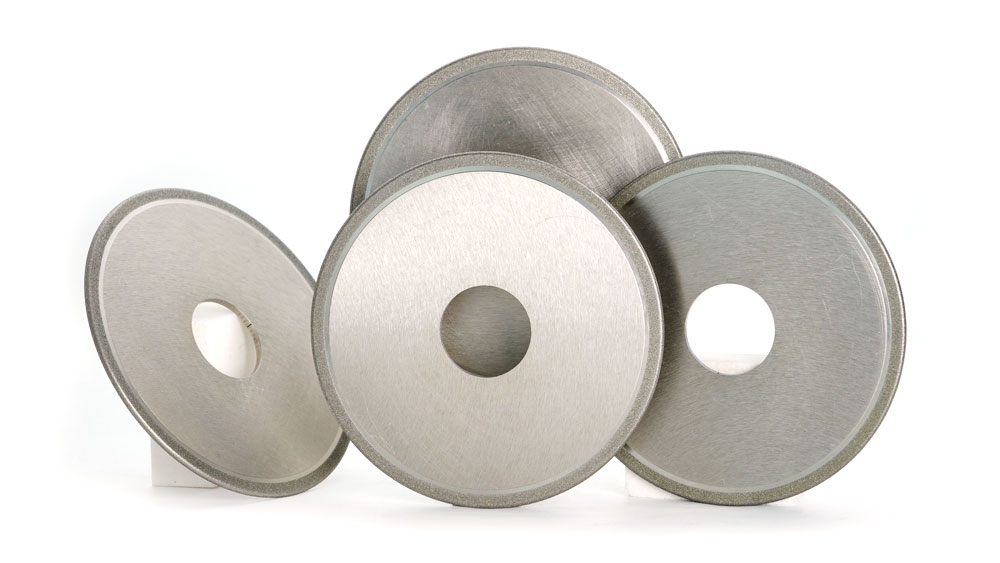

Diamond and CBN Electroplated Cutting Wheels
Below are the unique selling propositions that inform every potential buyer why they should purchase electroplated diamond and CBN cutting wheels:
- Feature free-faster cutting with less heating and no dressing because of the diamond particles that jut out from the surface.
- Retention of original dimensions and shape throughout the lifespan.
- Allow the re-plate of the body several times, making the dressing procedure unnecessary.
- A Flexible electroplated process with reduced investment and convenient manufacturing.
- High cutting efficiency with fantastic surface roughness and long lifespan.
Overview
Several industries that know the importance of cutting wheels always seek to get the right product to handle the operation efficiently. As it’s widely understood that the quality and functionality of the tools and how they can interact with workpieces will decide if a smart move is made when purchasing abrasive tools.
Electroplated diamond and CBN cutting wheels are great recommendations for metal manufacturing and fabrication operations for cutting material from different workpieces. So, it’s completely accurate if details about these cutting wheels are explicitly elaborated for the interest of every potential buyer.
Cutting Wheels
A cutting wheel can also be referred to as a “cut off wheel” or “cutting disc.” It is designed using an abrasive compound, and it works effectively to cut off materials such as aluminum and steel. It is characterized by fast-rate spin when used with a grinder such as an angle grinder, die grinder, or chop saw.
There are numerous tools that use these wheels for material from a workpiece in metal manufacturing and fabrication operations.
Cut-off wheels or cutting wheels are completely different from grinding wheels with respect to their respective structure and function. Cutting wheels are typically used to cut material at 90-degree angles precisely and narrowly while grinding wheels employ an abrasive to work on a workpiece in grinding off large parts of the material.
Structurally, cutting wheels are not as thick as grinding wheels. Although these cutting wheels lack the lateral strength needed for side grinding, they feature minimal thickness that puts them in a better position to cut accurately and clean.
There are a few different materials that typically make up the cutting wheels. These mainly include the grains (for cutting), the bonds (for holding the grains), and the fiberglass (for reinforcing the wheels).
Bond
The bond is a substance for a cutting wheel that helps hold the grains in a proper position. It’s common to see manufacturers talking about the grade or hardness. This grade does not only refer to how hard the abrasive grains are but also how hard the bond that holds the grains in place is.
From a general perspective, when a bond is very hard, it implies that the cutting wheel is automatically made to have a longer work-life; on the contrary, when the bond becomes very soft, the cutting wheel is automatically conditioned to have a shorter work life.
Some of the benefits users of a softer bond enjoy include shedding grains faster to offer a faster cut, holding grains in proper position even after they have become worn, revealing new and sharp grain, and increasing the cut rate of the wheel.
For a bond to handle several materials properly, there is a need to involve bonding systems that can help hold the abrasive grits to the wheel’s surface. Some of the most common bond cutting wheels include brazed bond cutting wheel, metal bond cutting wheel, resin bond cutting wheel, and electroplated bond cutting wheels.
Electroplated Cutting Wheels
Electroplated bond cutting wheels feature sharp cutting capability, high grain density, excellent precision, high efficiency, no dressing, etc. They are wheels that can be designed with a series of shapes and are perfect for specific operations characterized by strict requirements on dimension and geometry shape. In sum, they are great tools that help improve process efficiency and handle complicated operations that many tools may find difficult to process.
Diamond Electroplated Cutting Wheels
Electroplated diamond cutting wheels are used when there is a need to achieve precision and more efficient cutting. The bond is suitable for both wet cutting and dry cutting. Specifically, they are cutting wheels for cutting ceramics, glass, tungsten carbide, quartz, alloy material, etc.
Application of Electroplated Diamond Cutting Wheels
Check below to see the different ways electroplated diamond cutting wheels can be applied:
- Electroplated diamond cutting wheels are usually used to cut granite, marble, GRP, thermosetting plastics, electro carbons, pre-sintered and pre-fired materials, PVC and pc boards, graphite, fiberglass, soft ferrites, etc.
- There are some electroplated diamonds with more SuperHard saw blades. These blades are attached to circular saws, angle grinders, and handheld saws to cut marble, granite, etc.
Features of Diamond Electroplated Cutting Wheels
The following are the common features of electroplated diamond cutting discs:
- High sharp cutting performance with less heat generation
- Smoother cutting on plastic, ceramic tiles, fiberglass through continuous rim cutting discs
- Better cutting effect when it is compared with a sintered diamond saw blade and don’t lead to the broken edge
- Better cutting of granite, marble, and abrasive materials via segmented rim cutting discs.
- The typical slot types of the segmented rim are the “U” and “Keyhole” shape slots.
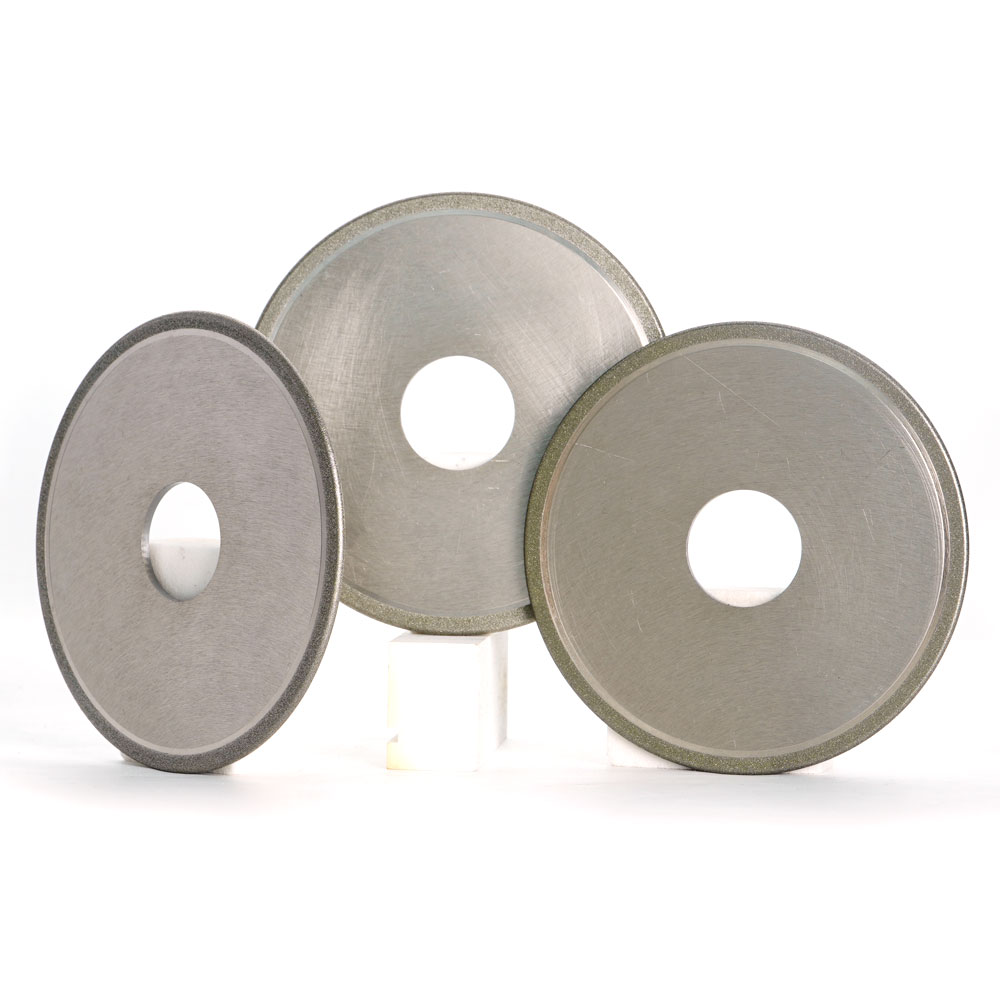
Specifications of Diamond Electroplated Cutting Wheels
There are different diamond electroplated cutting wheels with their peculiar and popular specifications. Manufacturers can also make other types and sizes of diamond cutting discs according to customers’ requirements.
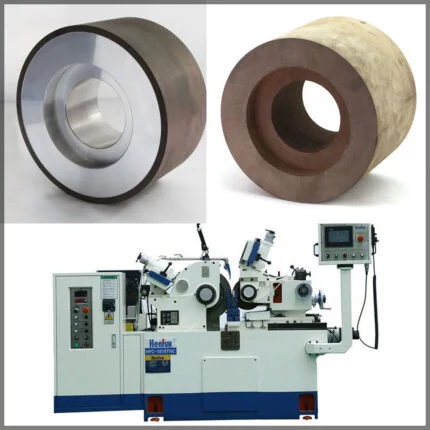
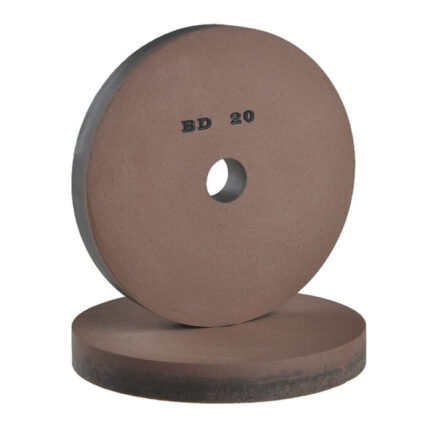
| Cutting Wheels Photo |  |
 |
 |
| Outer Diameter | 12″ (300 mm)– 20″ (500mm) | 4″ (100 mm) – 9″ (230 mm) | 4″ (100 mm) – 9″ (230 mm) |
| Arbor hole (mm) | 25.4 30 50 | 5/8″-11 Flange | 22.23 |
| The thickness of the steel core | 1.8mm 2mm – 3.0mm | 1.4mm – 1.6mm | 1.4mm – 1.6mm |
| Rim | Continuous Segment | Continuous Segment | Continuous Segment |
CBN Electroplated Cutting Wheels
Like diamond electroplated cutting wheels, the CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) cutting wheels are employed when achieving precision, and more efficient cutting is highly needed. They are also ideal for both wet cutting and dry cutting. However, electroplated CBN cutting wheels are cutting wheels specifically made for cutting for metal and steel and other similar materials.
Application of CBN Electroplated Cutting Wheel
Check below to see how electroplated CBN cutting wheels can be applied:
- Cubic Boron Nitride is an excellent cut-off wheel that suits cutting hardened steel, mold steel, high cutting, stainless steel, tool steel, and any ferrous metals.
- The tool is ideal for high-speed cutting applications, based on its high rigid core.
Features of CBN Electroplated Cutting Wheels
When it comes to discussing great tools designed specifically to handle superalloy and hardened ferrous materials, CBN and diamond can never be set aside. In fact, they are on top of the list. Cubic Boron Nitride is next to diamonds on the scale of hardness. It provides about five times the abrasion resistance offered by its traditional counterparts.
Below are the common features of electroplated CBN cutting discs:
- Offer users taut dimensional management of tools that provides polished surface finishes
- Does not create any bit-dulling grit
- Excellent chemical resistance and thermal conductivity
- Provides high stock removal
- High quality and improved wheel life
- Grit concentrations of 100% (high), 75% (medium), and 50% (low).
- Superabrasives come in different grit sizes, including D181 – D126 (coarse), D107 – D76 (Medium), D64 – D54 (Fine), and D46– D25 (Extra Fine)
Specifications of CBN Electroplated Cutting Wheels
The table below contains the overall specification of Cubic Boron Nitride:
| Density | 3.48 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 75–90 GPa |
| Thermal stability | 1,573–1,673 K |
| Thermal conductivity | 1.3 kW/m·K |
| Melting point: | 3,500 K (10.5 MPa) |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Below are questions worthy of being reviewed. The answers should provide additional details for further clarity.
What are the grit sizes for diamond electroplated cutting wheels?
The grit sizes used with electroplated diamond cutting discs range from D 64 to D 427. These sizes help cut hard materials such as ceramics, tungsten carbide, and fiber-reinforced plastics.
What Material can be worked by diamond electroplated cutting wheels?
The material worked by diamond electroplated cutting wheels includes fiber-reinforced duroplastics (GRP, CRP) and technical ceramics.
Do CBN wheels have superior thermal performance?
Experts show that the thermal stability of CBN is a significant advantage over the diamond. While Cubic Boron Nitride does not change at over a thousand degrees, diamond starts to lose a tremendous amount of hardness at 700 degrees.
Are diamond wheels harder than CBN wheels?
Most users preferred diamond wheels when working on hard superalloys. However, due to the carbon makeup of diamond, the wheels could end up dissolving iron when the temperature is high.
On the contrary, CBN wheels do not feature too much carbon, making them perfect when working on hardened steel tools. With CBN wheels, high levels of accuracy can easily be maintained while cutting off high amounts of material under extreme heat. This makes CBN wheels a better alternative to diamond wheels when machining ferrous metals.
Wrapping up
In a nutshell, electroplated cutting wheels are powerful tools to carry out special cutting operations efficiently. With the proper application and usage of electroplated diamond cutting wheels and electroplated CBN cutting wheels, you can have a flexible cutting process faster. Besides, they are tools with a long lifespan, which helps reduce the cost spent on manufacturing them. The details in the content should expose you to how the high-quality tools can meet your satisfaction as far as the cutting process is concerned.
More other customized cutting wheels are available, contact us.
[wpforms id=”4612″]



























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.