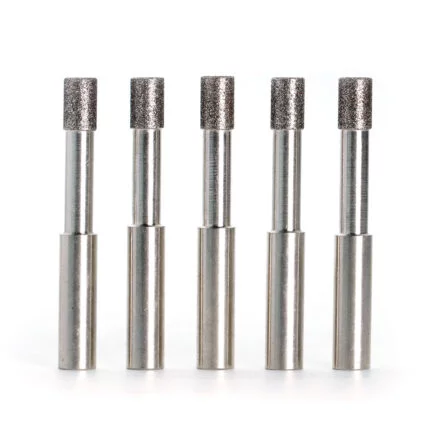
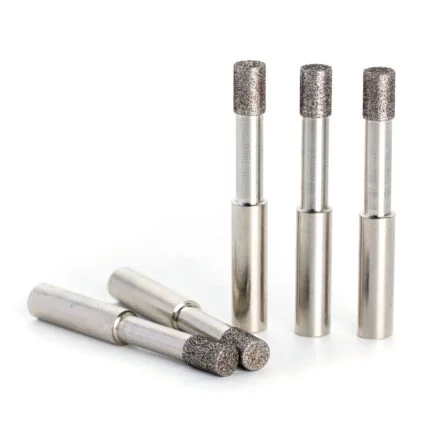
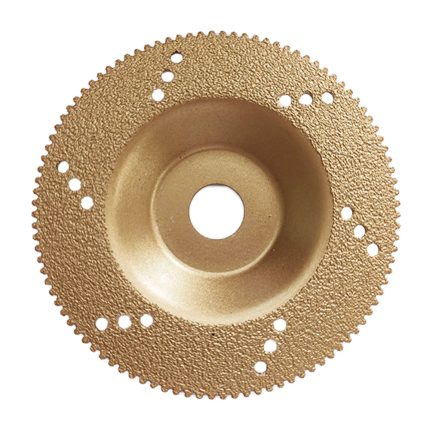
Brief Introduction of Diamond Honing Tools Expert Bore Finishing:
Diamond honing tools are being used to achieve a precision surface. These honing tools are made up of abrasive grains that are adhered together with a bond. Honing grains are unevenly shaped and range in size from 10 to 50 micrometers in diameter (300 to 1500 mesh grit). Smaller grain sizes result in a smoother workpiece surface.
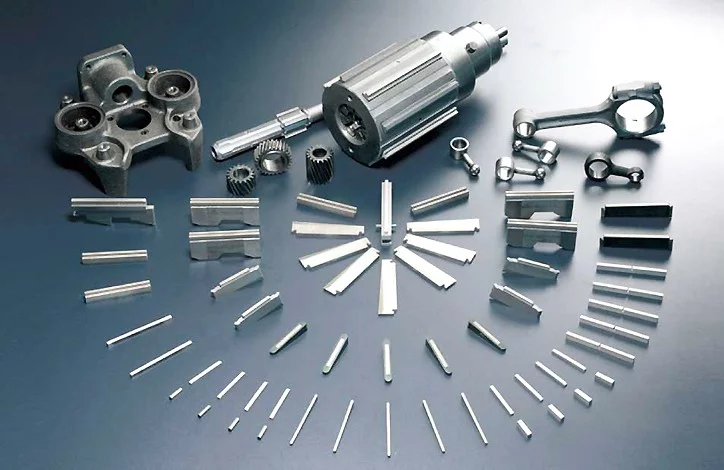
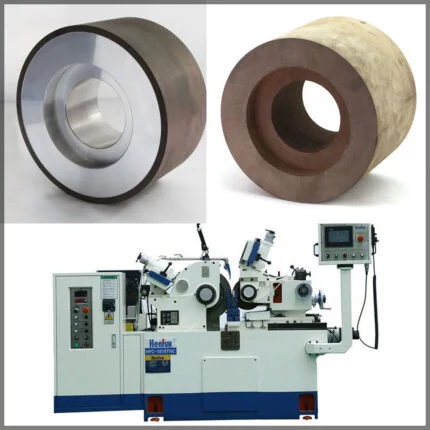
Compared to traditional abrasives, these honing tools can withstand higher operating pressures and surface speeds. The diamond honing tool’s job is to transfer the power generated by the machine to the workpiece. Honing can improve the taper, size, finish, and straightness of a bore. A spindle nose adaptor, a driving shaft, and the honed body make up the tool. Abrasive items such as hones and honing tools are used to polish the finish of internal bores and exterior surfaces. Flexible hones, hand hones, and honing sticks or tools are the three fundamental types of diamond honing tools. The major field of use has been honing tungsten carbide and ceramics, where standard vitrified abrasives have failed due to the material hardness. In certain other cases, using diamond hones can save money on honing.
Features of Diamond Honing Tools:
- Engineered and built to improve the efficiency of a wide range of finishing operations.
- Super abrasive honing products
- Environmental friendly with less noise
- Cost-effective with high performance
- These diamond honing tools can work with diameters ranging from 1,52 to 1524 mm (.060 to 60 inches)
- Fast action with more strength and durability
- Crafted from the highest quality materials
Detailed Description of Honing and Diamond Honing Tools:
-
Definition of Honing:
Honing is defined as the act or process of sharpening something on a hone or whetstone. Honing the sharp edge does not affect the exact alignment of the cutting machine’s knife. On the inside of tubing or cylinder bores, the honing process gives the final size and develops the required finish pattern. Finishing is done by rubbing abrasive stones with the appropriate grit and grade against the work surface. Under regulated pressure, the stones are rotated and reciprocated in the section with hone abrasive. The surface of the honed portion has a cross-hatch pattern created by combining rotation and reciprocation.
-
Purpose and Parts of Diamond Honing Tools:
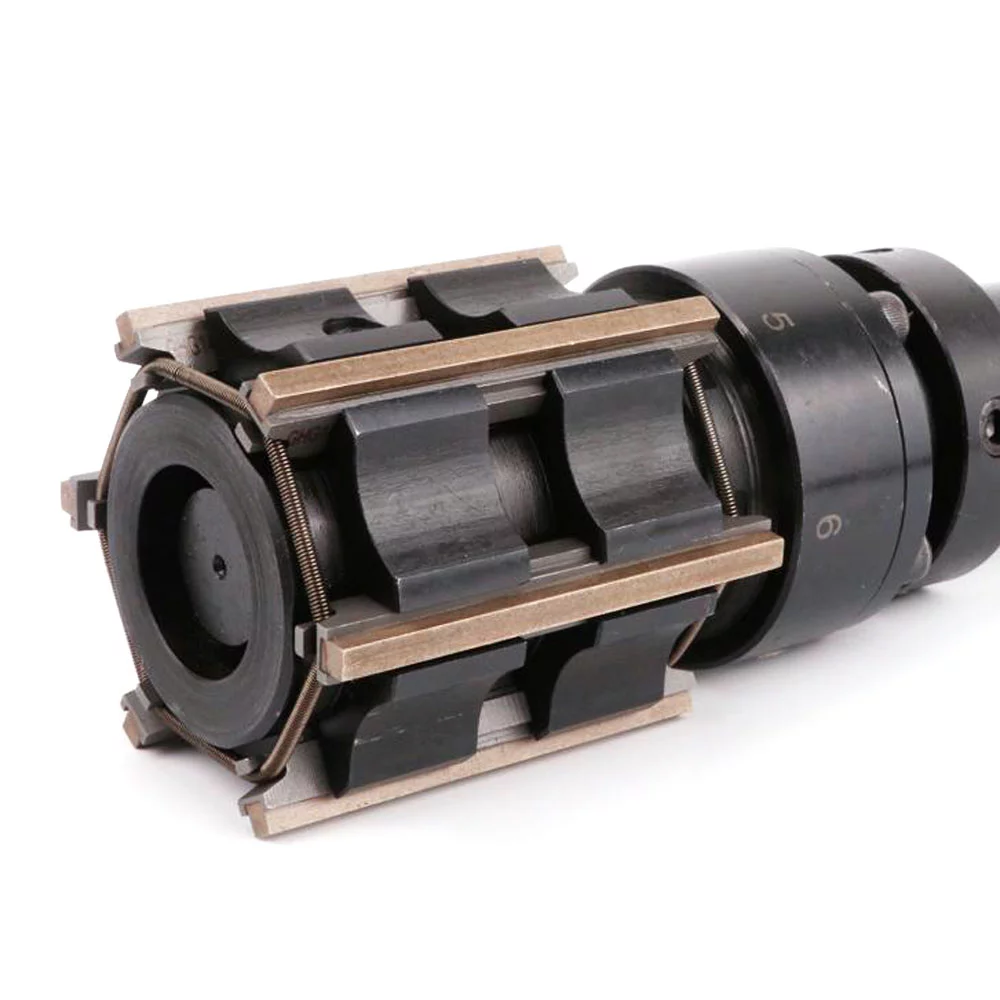
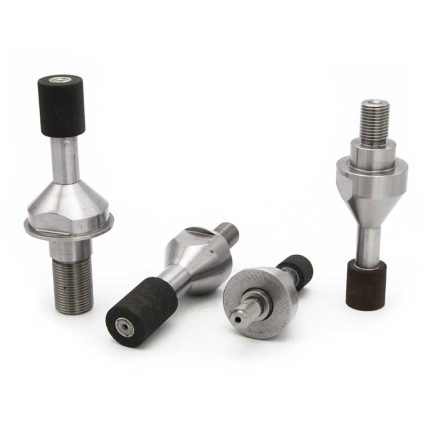
The honing tool’s job is to transfer the power generated by the machine to the workpiece. Honing can improve the taper, size, finish, and straightness of a bore, but it doesn’t usually fix axial alignment or placement. A spindle nose adaptor, a driving shaft, and the honed body make up the tool. A cone is linked to a push rod in the honed body. A motor or hydraulic cylinder moves the pushrod within the driving shaft up and down in the honing body. The head is where the actuator is positioned. As the cone descends, the expansion plates are pushed outward, enlarging the stones. The stock material is removed from the workpiece using abrasive stones. The garter springs retain the stones in place in the tool and collapse them when the diamond honing tool is withdrawn from the bore.
Hone Guides for Diamond Honing tool:
Diamond honing tool comes with hone guides. They protect the hone stones by preventing the metal of the honing tool from hitting the bore surface when entering or exiting the bore.
Bushing of Hone Guide:
The hone guide bushing’s purpose is to direct the honing tool into the bore’s center. Typically, the bushing is constructed of hardened steel or carbide.
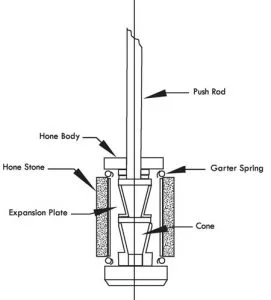
(Parts of Honing machine associated with diamond honing tools)
Adjustable Cone:
An adjustable cone can be used to extend the bottom of the stones to account for wear and retain the bottom at size while honing blind bores.
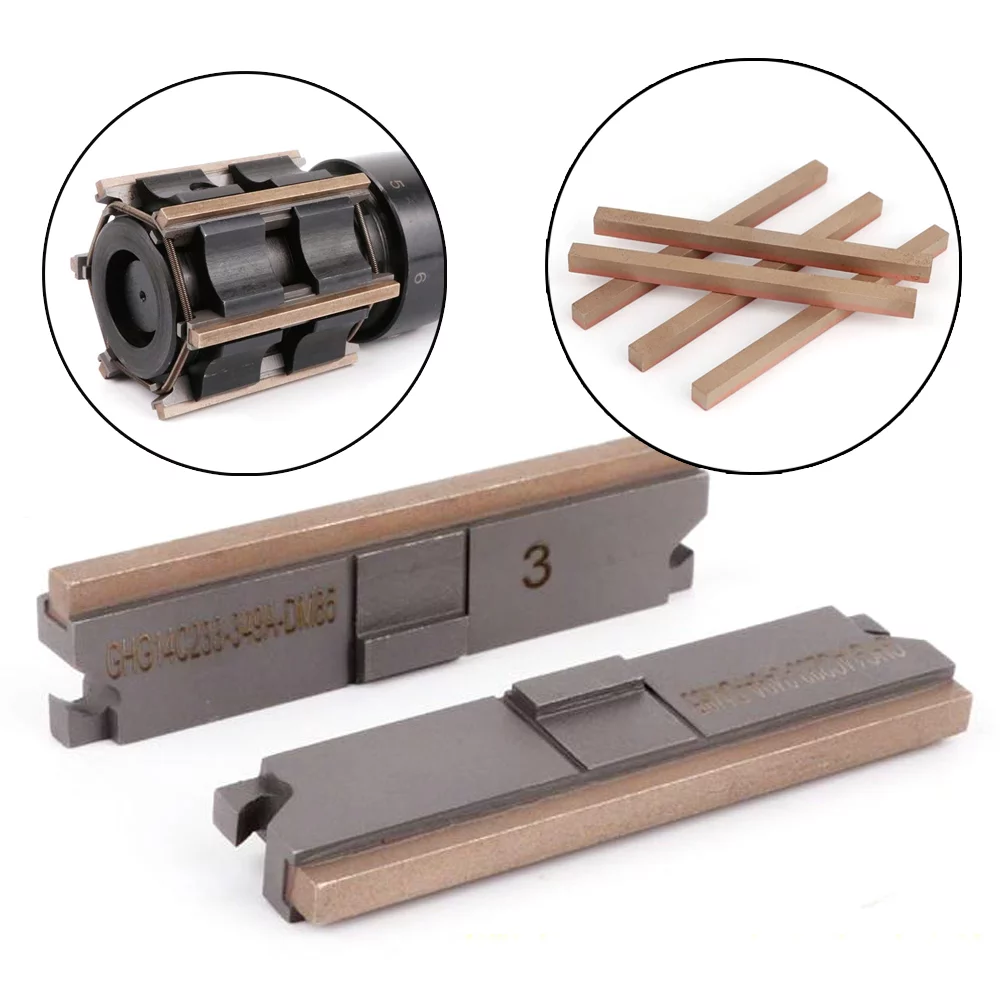
3. Manufacturing of Diamond Honing Tools:
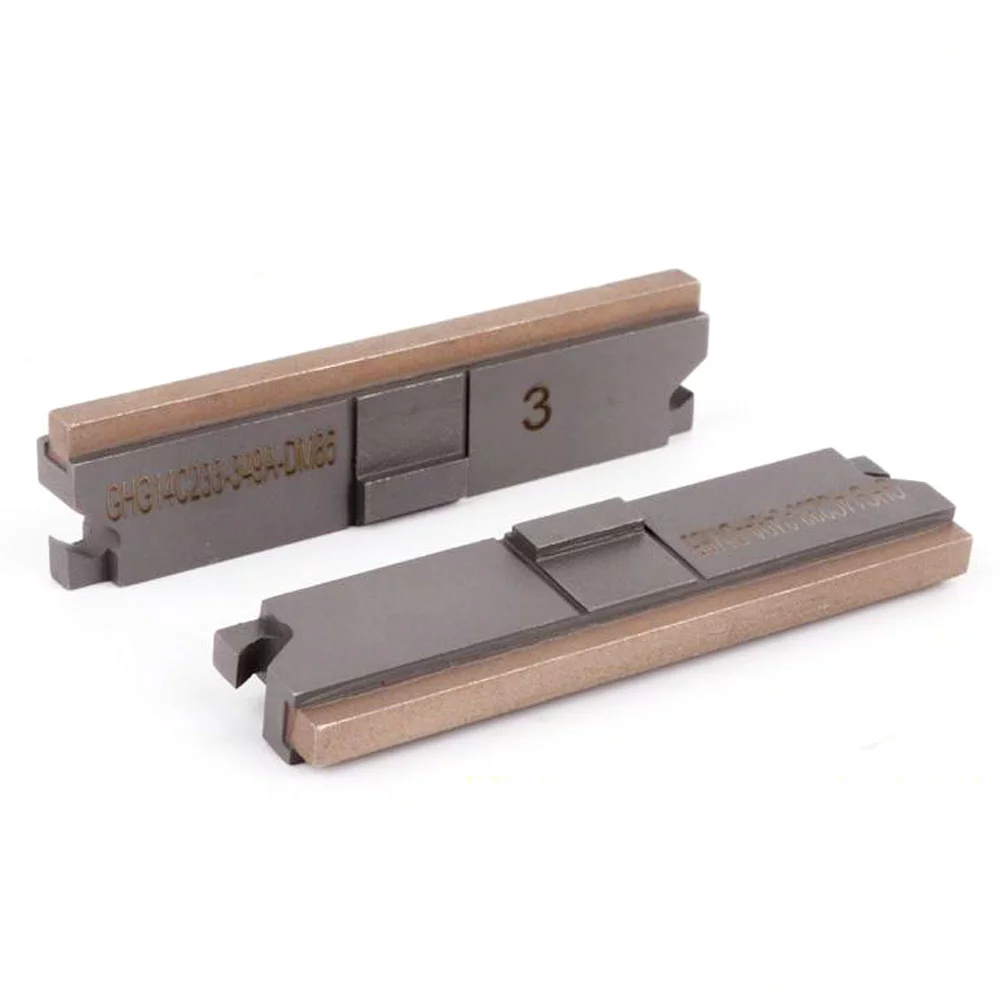
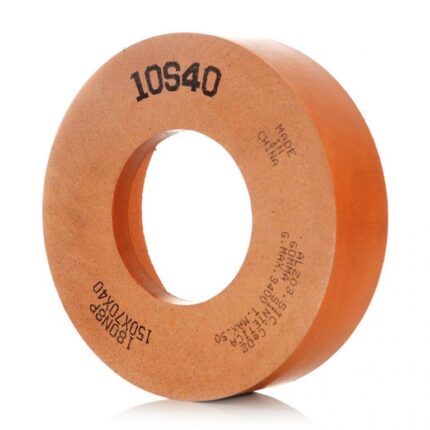
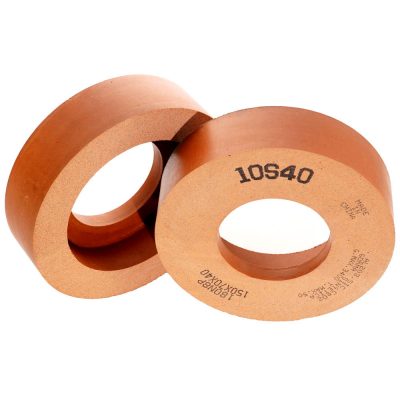
A diamond abrasive boring bar, made of an extensible soft cast iron sleeve permanently covered with 100/120 grit natural diamond abrasive, or a sintered sleeve with abrasive incorporated in it, used as the honing tool.
4. Types of Bonds Used to determine Hardness of Diamond Honing Tools:
Cobalt Iron Bond (M):
A strong bond for tungsten carbide with a cobalt concentration greater than 25%. It is used in the honing tools for ceramic glass and iron.
Bronze Bond(MB):
A medium bond that is utilized on most heat-treated steels above HRC63 and is used for tungsten carbide with a cobalt concentration of 11 to 25%.
Resinoid Bond (S4):
A soft bond for tungsten carbide with a cobalt percentage greater than 11%, as well as other highly hard materials.
5. Types of Diamond Honing Tools:
There are three types of diamond honing tools. Each has unique use and properties.
-
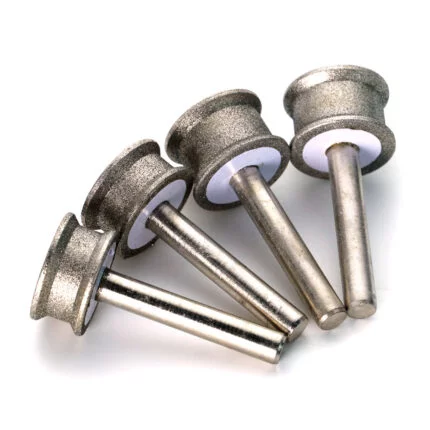
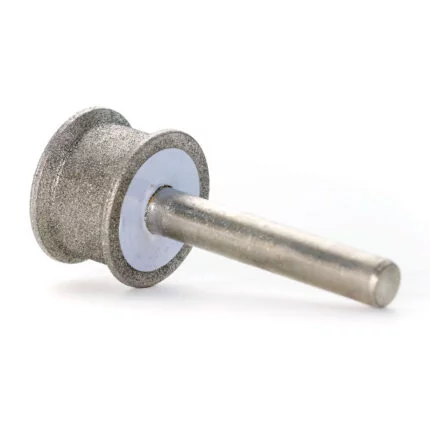
Flexible Hons:
Abrasive beads are attached to the ends of the bristles of flexible hones. They are used to smooth or polish the finish of interior or exterior surfaces, just like other hones and honing instruments.
-
Hand hones
known as diamond hones, are used to sharpen ground cutting-tool edges offhand.
-
Honing Sticks:
Internal bores are finished with honing sticks or honing tools. Internal grinding involves polishing or completing the surface of a part’s interior diameter with smaller-diameter wheels or abrasive materials.
6. Advantages of Honing With Diamond honing tools:
- Less complicated or low-priced fixtures
- It’s quite accurate.
- Both long and short bores may be used with it.
- It keeps the bore’s original centerline.
- Any material, regardless of its hardness, may be finished.
- There are no chucking or locating mistakes because the workpiece does not need to be turned by power, and no chucks, faceplates, or rotating tables are required.
- Because the hone is powered by a central shaft, bending the shaft will not result in tapered holes, as it does when boring.
Diamond Honing Tool vs Diamond Wheel
- If the prior processes left enough stock for the hone to clear out all the imperfections, the result is a completely round hole with no taper or high or low regions.
- When compared to grinding or fine boring, which employs a tiny contact area at a high speed, honing uses a big contact area at a moderate speed.
- The crosshatched pattern formed by the simultaneous rotating and reciprocating action is good for retaining lubricant.
- Diamond stones, similar to diamond wheels, may be used to hone diameters with 0.001 to 0.0001 inch and closer accuracies.
7. Benefits of Diamond Abrasive for Making Diamond Honing Tools:
The hardness of Diamond Abrasive:
Diamonds, coal, and graphite are all made up of the same chemical elements. The carbon atoms in coal and graphite are organized in sheets. Coal and graphite have a velvety feel because of this. Diamonds, on the other hand, are crystalline carbon. The carbon atoms in diamonds are organized in a tetrahedron. In three-dimensional space, this configuration indicates that each carbon atom is connected to five other carbon atoms. Carbon sheets in graphite and coal are substantially weaker than this. Diamond honing tools are so hard because of the chemical structure that they can cut through any substance, including other diamonds.
Durability:
Resin diamond abrasives and metal bond diamond abrasives both are used preferably because the bond (metal or resin) gradually wears away, exposing fresh layers of diamond to polish the concrete. The tool’s durability is determined by the bond, not the diamond. The diamonds eventually fall out of the tool. Some of these are even ground down by the tool’s other diamonds. Diamond tools, on the other hand, endure longer than other abrasives due to their hardness. So diamond honing tools are preferred to other types of honing tools.
Speed Cutting:
Diamond’s hardness also implies that diamond abrasives grind more quickly than other abrasives. Part of this is related to durability – grinding tasks take less time when there are fewer tool replacements. Diamond tools’ quickness, on the other hand, is because they cut through any other substance. Diamond honing tools will grind directly through a particularly tough stone, rather than grinding it repeatedly.
Cost-effective:
Industrial diamonds are a cost-effective tool material, despite their appearance. Other abrasives are more expensive than diamonds. They do not, however, cost so much more than they are prohibitively expensive. Diamond abrasives also allow for more work to be done with fewer tool changes because of their endurance. This implies that diamond honing tools are equivalent to other abrasives in terms of cost while having more grinding power. These Diamond honing tools are cost-effective tools for polishing and bore finishing because of their hardness, durability, and speed.
Summary:
Bore finishing is a demanding process and diamond honing tools are widely used for this purpose. Diamond abrasives are preferred because of their hardness and durability. The objective of the diamond honing tool is to transfer the machine’s power to the workpiece. A bore’s taper, size, finish, and straightness can all be improved by honing. The tool is made up of a spindle nose adapter, a drive shaft, and the honed body. Diamond honing tools of all types with all three types of bonds are available. We can choose a honing tool with the desired bond, depending on the nature of our work.
More customized diamond tools are available, contact us.
[wpforms id=”4612″]


























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.